Relax frog mac os. Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on March 16, 2020.
Applies to the following strengths: 500 mg; 750 mg; 100 mg/mL
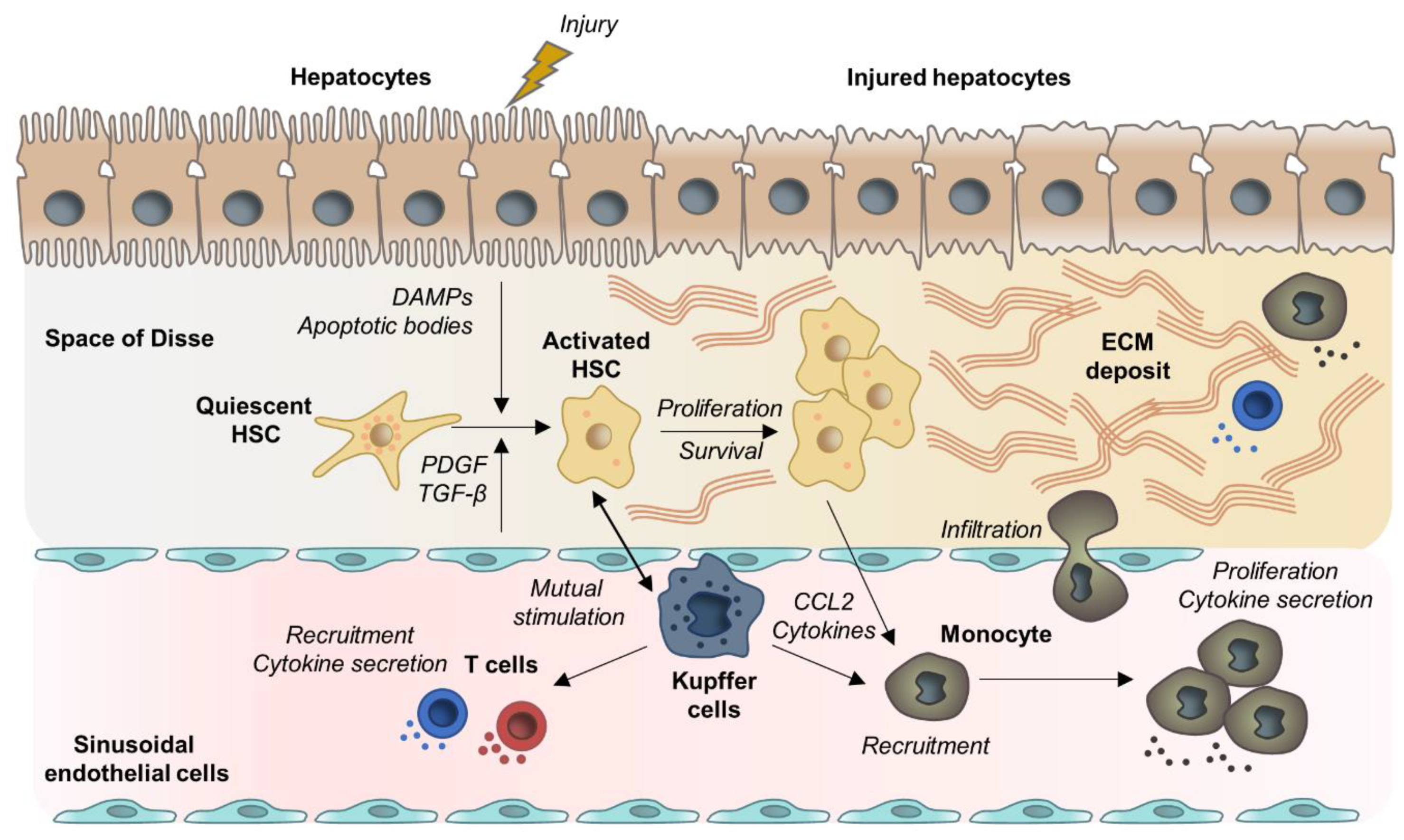
Version:AVerMedia CamEngine Lite(Mac) Beta v1.1.0.7 Beta OS:macOS 10.15/11.0; Description: CamEngine Lite covers essential functions such as Brightness, Sharpness, Contrast, Saturation, and Hue adjustments.Due to macOS restriction of virtual device, some software could not use CamEngine as video source. Issues closed: 1. MAC infection is a serious condition that can cause damage to the lungs. MAC infection is not contagious. Common signs and symptoms of MAC lung disease include fatigue, chronic cough, shortness of breath, night sweats, coughing up blood and weight loss. Symptoms may persist or worsen despite being treated for another lung condition.
Usual Adult Dose for:
Usual Pediatric Dose for:
Additional dosage information:
Usual Adult Dose for Muscle Spasm
ORAL:
Initial Dose: 1500 mg orally 4 times a day
-Doses of 6000 mg per day are generally used for the first 48 to 72 hours
-In severe cases, doses up to 8000 mg per day may be used
Maintenance dose:
500 mg tablets: 1000 mg orally 4 times a day
750 mg Tablets: 750 mg orally every 4 hours OR 1500 mg orally 3 times a day
PARENTERAL:
-For the relief of moderate symptoms: 1 g IV or IM once, then switch to oral
-For relief of severe symptoms or postoperative conditions: 1 g IV or IM every 8 hours
Maximum Dose: 3 g in 24-hours
Maximum Duration: 3 consecutive days; may repeat after a drug-free interval of 48 hours
Comments:
-Higher doses are recommended in the first 48 to 72 hours of treatment, then doses can usually be reduced to approximately 4000 mg per day.
-Oral tablets should be administered whenever feasible; IV/IM therapy should not be administered for more than 3 consecutive days without a drug-free interval of 48 hours.
Use: As an adjunct to rest and physical therapy for the relief of discomfort associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions.
Usual Adult Dose for Tetanus
Initial dose: 1 to 2 g IV followed by an additional 1 to 2 g via IV infusion
Maximal Initial Dose: 3 g
Repeat initial IV dose every 6 hours until NG tube or oral therapy is possible
Once NG tube is in place, may crush tablets, suspend in water or saline and administer through tube
-Total oral doses of up to 24 g may be needed based on patient response
Comments:
-There is clinical evidence to suggest this drug may have a beneficial effect in the control of the neuromuscular manifestations of tetanus.
-This drug should not replace the usual procedure of debridement, tetanus antitoxin, penicillin, tracheotomy, attention to fluid balance, and supportive care; if used, this drug should be added to the regimen as soon as possible.
Use: To control the neuromuscular manifestations of tetanus.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Tetanus
Initial dose: 15 mg/kg or 500 mg/m2 IV; repeat initial dose every 6 hours as needed
Maximum dose: 1.8 g/m2/day IV for 3 consecutive days
Maintenance dose: May be given by injection into tubing or by IV infusion with an appropriate quantity of fluid
Comments:
-There is clinical evidence to suggest this drug may have a beneficial effect in the control of the neuromuscular manifestations of tetanus.
-This drug should not replace the usual procedure of debridement, tetanus antitoxin, penicillin, tracheotomy, attention to fluid balance, and supportive care; if used, this drug should be added to the regimen as soon as possible.
Use: To control the neuromuscular manifestations of tetanus.
Renal Dose Adjustments
Oral therapy: No adjustment recommended
Injectable therapy: Not recommended in patients with renal insufficiency due to the high concentration of polyethylene glycol in the solution
Liver Dose Adjustments
Use with caution, dose adjustment may be required, especially in patients with cirrhosis; however, no specific guidelines have been suggested
Precautions
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
-Hypersensitivity to active substance or any product excipients
-Known or suspected renal pathology (injection; due to presence of polyethylene glycol 300 in the vehicle)
Safety and efficacy or oral therapy have not been established in patients younger than 16 years.
Safety and efficacy or injectable therapy have not been established in patients younger than 18 years, except in tetanus.
Consult WARNINGS section for additional precautions.
Dialysis
Data not available
Other Comments
Administration advice:
Oral Therapy: Take orally with or without food
Injectable Therapy:
-For IV and IM administration only; do not administer subcutaneously
-Total daily dose should not exceed 3 g per day (3 vials) for more than 3 consecutive days except in the treatment of tetanus; see below for special directions for use in tetanus
For IV Administration:
-May administer undiluted IV directly into vein at a maximum rate of 300 mg/minute (3 mL/minute)
-May dilute and administer via IV infusion using normal saline or D5W; 1 g (1 vial) should be diluted in no more than 250 mL
-Use caution to avoid vascular extravasation; this hypertonic solution may cause thrombophlebitis
-Patient should remain recumbent during and for at least 10 to 15 minutes following injection
For IM Administration:
-Inject no more than 500 mg (5 mL) into each gluteal region
-Injections may be repeated at 8-hour intervals; switch to oral therapy as soon as feasible
Special Directions for Use in Tetanus:
-Inject 1 or 2 g (10 or 20 mL) directly into tubing of inserted indwelling needle.
-Add 1 or 2 g (10 or 20 mL) to infusion bottle to allow for a total of 3 g (3 vials) as initial dose
Storage requirements:
-Once IV infusion is prepared: Do not refrigerate
IV compatibility: Compatible in normal saline and dextrose 5% solution
General:
-Polyethylene glycol 300 is present in the injectable formulation; large doses of polyethylene glycol 300 are known to increase preexisting acidosis and urea retention in patients with renal impairment; while the amount present is within the limits of safety, use is contraindicated in patients with renal impairment out of an abundance of caution.
Patient advice:
-Patients should understand that this drug may impair their mental and/or physical abilities to perform hazardous tasks such as driving, and they should be counseled appropriately.
-Patients should understand that this drug is a CNS depressant and patients should be cautioned about concomitant use of alcohol or other CNS depressants.
-Patients should be instructed to speak with their healthcare provider if they are pregnant, intending to become pregnant or breastfeeding.
Frequently asked questions
More about methocarbamol
- During Pregnancy or Patient Tips
Consumer resources
- Other brands
- Robaxin, Robaxin-750
Professional resources
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Continuing Education for MRI Technologists, Radiologic Technologists, and other Medical Imaging Professionals.
6019-207 MRI Liver Imaging: What, Why, & How
This online activity was recorded at the ARMRIT 2019, Semi-Annual Meeting, Golden Nugget Hotel & Casino, Las Vegas, NV Nov. 1 & 2
| Format: | On-line Seminar Lectures | Certificates of Credit accepted by American Registry of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologists (ARMRIT) and the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) |
| RT Credit: | 1.00 ARRT Category A | |
| Tuition: | $ 15 |
Educational Objective
The purpose of this presentation is to familiarize the audience with the anatomy and physiology of the liver, describe some of the common diseases of the liver, and how it all directs the way we image the liver. Included in the presentation will be contrast media focused on Gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents.
Outline:
- Liver anatomy and physiology
- Location, size, shape
- Blood supplies
- Venous drainage
- Lymph drainage
- Cellular level anatomy and physiology
- Use of T1W and T2W images
- Role of diffusion in liver imaging
- Cancer
- Infection
- Why contrast enhanced liver exam?
- Carcinomas
- Metastasis
- Infections
- Other cancer
- Timing of post-contrast imaging
- Early arterial, late arterial, venous, hepatobiliary
- Techniques for specific timing
- Guessing!
- TestBolus
- CareBolus
- TwistVIBE
- Use of hepatocyte-specific agents (HSA) and non….
- What is this?
- Multihance/Eovist
- How does it change the outcome
- Why one or the other?
- Hepatocytes or extracellular areas of interest?
- Hepatobiliary timing
- Opportunity for CE MRCP post-HAS
- What is this?
- Motion suppression techniques
- Breath-hold
- Trigger/gate
- BLADE/PROPELLER
- SSTSE and SSFP GRE (TrueFISP)
Continuing Education Credit
This program has been approved by the Association for Medical Imaging Management (AHRA) for 1.0 hours ARRT Category A continuing education credit.
Certificates of Credit are accepted by the American Registry of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologists (ARMRIT) and the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT).
Tuition
ICPME accepts American Express, MasterCard, and Visa.
Tuition for this course includes unlimited access to the course and your Certificate of Credit.
Please note: tuition payments are non-refundable.
How to Enroll and Participate
Estimated time to complete this activity is 1.00 hours.
- Click ENROLL NOW, CONTINUE through the shopping cart, CONFIRM ORDER, and ACCESS COURSE NOW.
- Once you are enrolled, you can return to this course anytime by logging to your account at www.icpme.us.
- To access the course, click on MY ACCOUNT, then click on the course title.
Liver Mac Os 7
How to Receive Credit
Mac Os Catalina
- To access the posttest and evaluation, login to your account at icpme.us and click on the course title.
- Click the icons for POSTTEST and for EVALUATION.
- A passing grade of at least 75% is required to receive credit. You may take the test up to three times.
- Upon receipt of a passing grade, you will be able to print a certificate of credit from your account at icpme.us.
Your online account serves as a permanent record of credit certificates earned through icpme.us.
Questions?
Contact ICPME:
information@icpmed.com
Jointly Provided by
About the American Registry of
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologists
Because MRI is a Specialty

Consumer resources
- Other brands
- Robaxin, Robaxin-750
Professional resources
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Continuing Education for MRI Technologists, Radiologic Technologists, and other Medical Imaging Professionals.
6019-207 MRI Liver Imaging: What, Why, & How
This online activity was recorded at the ARMRIT 2019, Semi-Annual Meeting, Golden Nugget Hotel & Casino, Las Vegas, NV Nov. 1 & 2
| Format: | On-line Seminar Lectures | Certificates of Credit accepted by American Registry of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologists (ARMRIT) and the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT) |
| RT Credit: | 1.00 ARRT Category A | |
| Tuition: | $ 15 |
Educational Objective
The purpose of this presentation is to familiarize the audience with the anatomy and physiology of the liver, describe some of the common diseases of the liver, and how it all directs the way we image the liver. Included in the presentation will be contrast media focused on Gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents.
Outline:
- Liver anatomy and physiology
- Location, size, shape
- Blood supplies
- Venous drainage
- Lymph drainage
- Cellular level anatomy and physiology
- Use of T1W and T2W images
- Role of diffusion in liver imaging
- Cancer
- Infection
- Why contrast enhanced liver exam?
- Carcinomas
- Metastasis
- Infections
- Other cancer
- Timing of post-contrast imaging
- Early arterial, late arterial, venous, hepatobiliary
- Techniques for specific timing
- Guessing!
- TestBolus
- CareBolus
- TwistVIBE
- Use of hepatocyte-specific agents (HSA) and non….
- What is this?
- Multihance/Eovist
- How does it change the outcome
- Why one or the other?
- Hepatocytes or extracellular areas of interest?
- Hepatobiliary timing
- Opportunity for CE MRCP post-HAS
- What is this?
- Motion suppression techniques
- Breath-hold
- Trigger/gate
- BLADE/PROPELLER
- SSTSE and SSFP GRE (TrueFISP)
Continuing Education Credit
This program has been approved by the Association for Medical Imaging Management (AHRA) for 1.0 hours ARRT Category A continuing education credit.
Certificates of Credit are accepted by the American Registry of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologists (ARMRIT) and the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT).
Tuition
ICPME accepts American Express, MasterCard, and Visa.
Tuition for this course includes unlimited access to the course and your Certificate of Credit.
Please note: tuition payments are non-refundable.
How to Enroll and Participate
Estimated time to complete this activity is 1.00 hours.
- Click ENROLL NOW, CONTINUE through the shopping cart, CONFIRM ORDER, and ACCESS COURSE NOW.
- Once you are enrolled, you can return to this course anytime by logging to your account at www.icpme.us.
- To access the course, click on MY ACCOUNT, then click on the course title.
Liver Mac Os 7
How to Receive Credit
Mac Os Catalina
- To access the posttest and evaluation, login to your account at icpme.us and click on the course title.
- Click the icons for POSTTEST and for EVALUATION.
- A passing grade of at least 75% is required to receive credit. You may take the test up to three times.
- Upon receipt of a passing grade, you will be able to print a certificate of credit from your account at icpme.us.
Your online account serves as a permanent record of credit certificates earned through icpme.us.
Questions?
Contact ICPME:
information@icpmed.com
Jointly Provided by
About the American Registry of
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologists
Because MRI is a Specialty
The mission of the American Registry of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologists (ARMRIT) is to recognize individuals qualified as specialists and to promote high standards of patient care and safety in the diagnostic medical imaging modality of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) technology including: interventional MRI, cardiovascular MRI, functional MRI, and MRI breast imaging.
ARMRIT is the first certifying organization to:
1. Recognize MRI technology as a distinct medical imaging specialty utilizing non-ionizing radiation.
2. Require MRI clinical experience and competency for eligibility.
3. Promote formal MRI education with MRI clinical training.
4. Recognize MRI schools that offer full-time educational program leading to a career in MRI.
Certification through the Registry is open to qualified technologists in all imaging fields who have documented MR clinical experience and/or formal education completed through schools dedicated to MRI technologists.
For more information about ARMRIT or to apply for certification, visit ARMRIT.org.
DISCLAIMER
Participants have an implied responsibility to use the newly acquired information to enhance patient outcomes and their own professional development. The information presented in this activity is not meant to serve as a guideline for patient management. Any procedures, medications, or other courses of diagnosis or treatment discussed or suggested in this activity should not be used by clinicians without evaluation of their patient's conditions and possible contraindications and/or dangers in use, review of any applicable manufacturer's product information, and comparison with recommendations of other authorities.

